Liabilities
Liabilities are financial obligations or debts you owe to other people. These are amounts you must pay in the future and can come in many forms, such as loans, credit card balances, mortgages, and unpaid bills. Basically, debts are the opposite of assets: while assets are things you own that have value, liabilities are things you owe.
Types of Liabilities
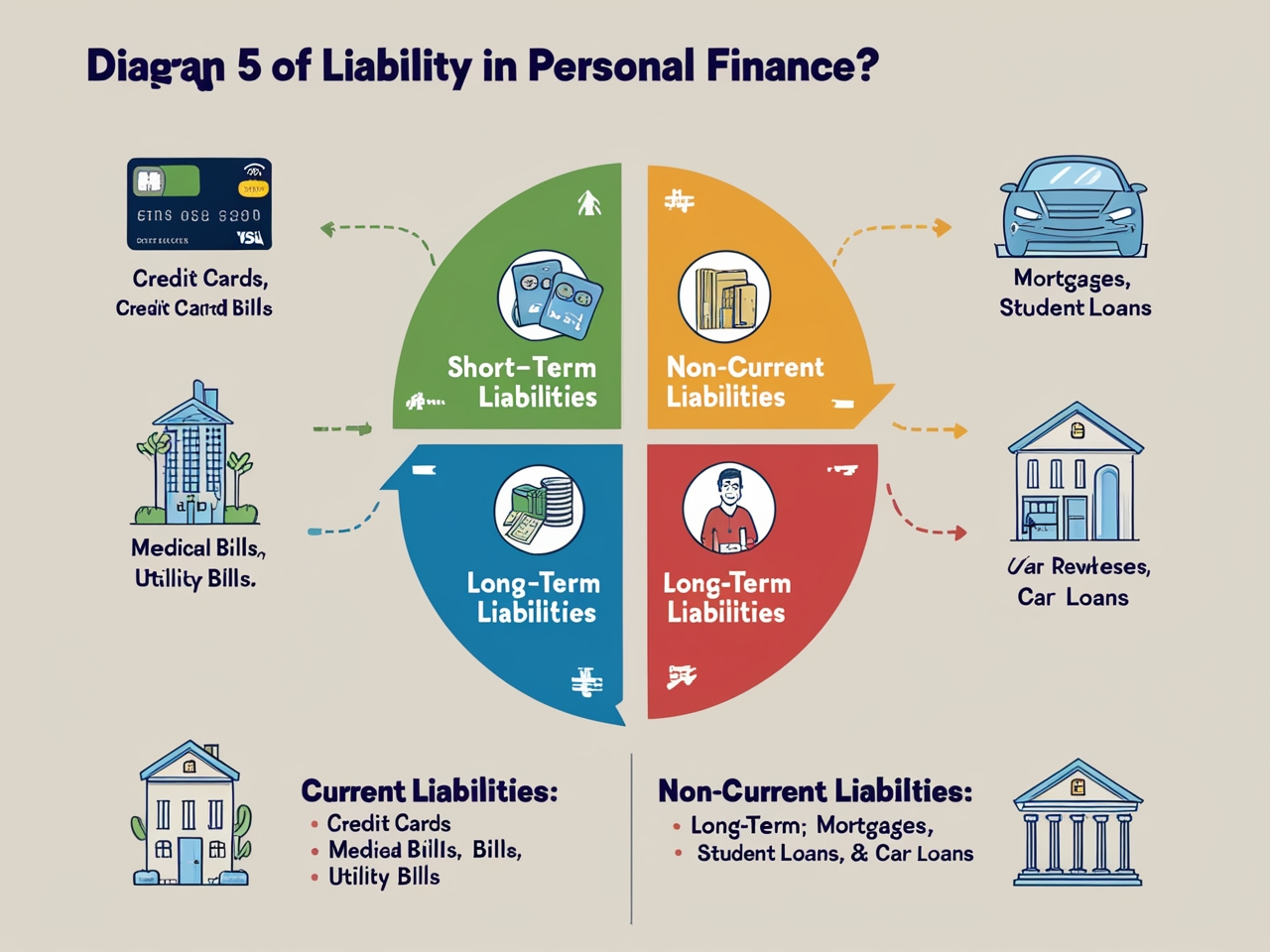
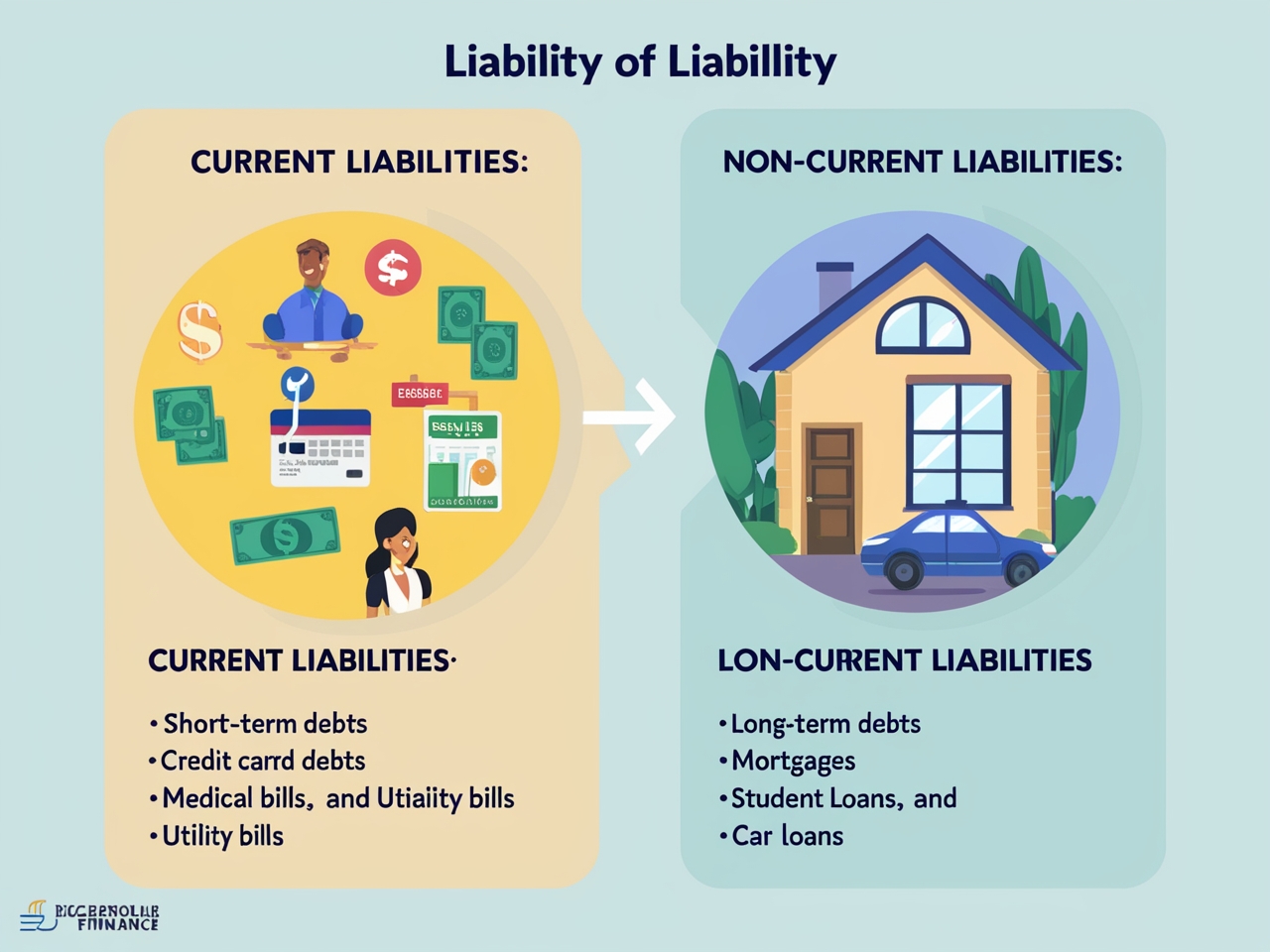
Liabilities can be divided into two main types:
Current Liabilities:
These are short-term debts or obligations that must be paid within one year. Some examples include:
- Credit card balances
- Short-term loans
- Utility debts
- Medical debts
Non-current Liabilities:
These are long-term debts or obligations that take more than one year to pay off. Some examples include:
- Mortgages
- Student loans
- Car loans
Why are Liabilities important?
Liabilities plays a vital role in your overall financial health. Understanding it will help you:
- Manage your debt: Managing your debt allows you to know how much you owe and to whom.
- Manage your cash flow: By knowing when and how much you owe, you can better plan your monthly expenses.
- Make informed financial decisions: If you’re considering taking on more debt or making investments, knowing your current debt will help you make smarter decisions.
How do liabilities affect your financial health?
Having too much debt can affect your financial stability. When your debts exceed your assets, it means you’re in debt and may be struggling to make ends meet. Here are some ways debt can affect you:
- Debt-to-income ratio: This ratio helps measure how much of your income is going toward paying off debt. A high ratio can indicate financial stress.
- Credit score: Unpaid debts can negatively impact your credit score, making it harder to get a loan in the future.
- Stress: Carrying a lot of debt can be stressful and make it difficult to save money for future goals.
How to manage Liabilities
- Create a budget: Track all your income and expenses, and see where you can cut expenses to make room for debt payments.
- Prioritize debt: Pay off high-interest debt (like credit cards) first, as it can grow quickly and out of control.
- Refinance or consolidate: If you have a lot of debt, consider consolidating it into one low-interest loan.
- Avoid getting into more debt: Be careful not to accumulate new debt, especially if you are already struggling with existing debt.
Conclusion
Debt is an important part of a person’s finances, but it should be managed carefully. By understanding your debt and keeping it under control, you can maintain a healthy financial life, make informed decisions, and achieve your long-term goals.